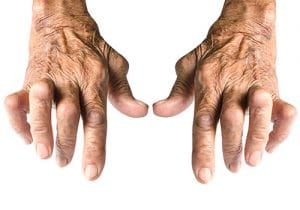
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Arthritis is any disorder that affects joints and organ tissues. It causes pain and inflammation. The joints most typically affected are usually inside the wrists, hands, knees, ankles, and feet. It may also affect different organs in the body especially the eyes, skin, heart, lungs, kidneys, system, and biological process tract. In this disease, the body attacks itself by mistake.
In rheumatoid arthritis, Inflammation causes fluid build-up within the joint creating the joints to swell.
Arthritis Treatment
Treatments for rheumatoid arthritis include exercise, occupational or physical therapies, medications, and surgery. The medication recommended by your doctor will depend on the severity of your symptoms, age, and medical history.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Advanced Explanation
Surgery is only needed when medications fail to prevent or slow the joint damage. Surgery may also help restore your ability to use your joint. It can also reduce pain and improve function.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune systemic inflammatory disease that affects up to 0.8% of the population, translating into 2.4 million Americans. It is caused due to genetic susceptibility and environmental factors as research has ascertained. It causes joint pain, stiffness, patterned symmetrical joint swelling of the fingers and wrists (being most common), deformities, X-ray damage, decreased function, poor quality of life, and disability. RA contributes to other diseases such as heart attacks and strokes.
The diagnosis is made based on the symptoms, examination, blood tests known as rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibody, X-rays, ultrasound, and MRI. Cortisone (e.g. prednisone) and NSAIDs e.g. ibuprofen, and naproxen can help symptoms but cannot modify the joint destruction and functional decline. They may cause stomach bleeding, poor kidney function, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular side effects among other side effects.
Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can drive the disease to a low activity state. The gold standard methotrexate at 15-25 mg per week, Arava, sulfasalazine, and the less potent Plaquenil are examples. But they often fail to induce remission. Newer biologic agents especially when used with methotrexate can produce good clinical outcomes. They include Enbrel, Remicade, Humira, Orencia, Rituxan, Cimzia, Simponi, and Actemra (listed in the order of approval by the FDA). However, most patients do not achieve remission from the disease even with these agents. These biological agents may cause mild and serious side effects which limit their use. More research is needed to devise better combination treatments with these agents and to identify more effective, safe, and less expensive drugs to help patients with RA. Better therapies can be discovered only when RA patients volunteer for clinical research trials.
The health care providers in practice at Regional Arthritis and Rheumatology Associates are dedicated to taking care of patients with RA. They constantly learning about the new rheumatology drugs that are on the horizon.
